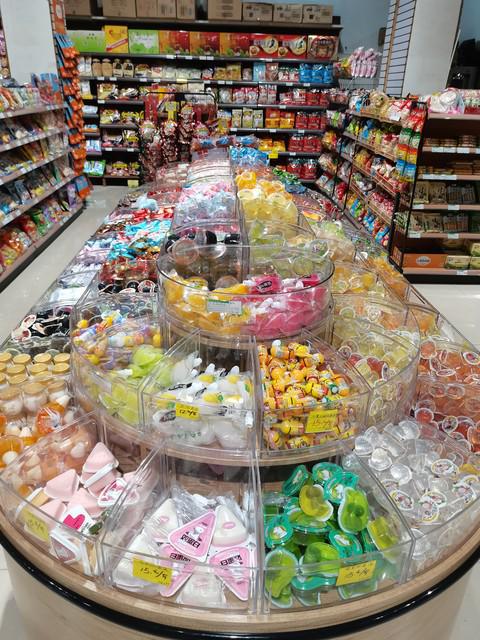
On the afternoon of the 13th, the breach in Yingli Town of Mihe River was about to be closed after the rescue and relief workers made great efforts to repair it. Qilu Evening News Qilu Yidian reporter Zhou Qingxian photo

On the 13th, in the Yangkou Town section of Mihe River in Shouguang, rescue and relief workers were blocking the gap. Qilu Evening News Qilu point reporter Zhou Qingxian Toarey Yang photo
On the afternoon of August 11th, influenced by typhoon "Lichima", the dam of the Mihe River in Shouguang was in danger, and the surrounding villages were affected. On the 13th, after more than 20 hours of intense rescue, the breach on the west bank of Mihe River in Yingli Town reached 8: 00 that night and the closure of Helong was completed. On the same day, due to the decline of the water level of the Mi River, the flow rate of the river at the breach continued to decline until the river basically stagnated, which provided favorable conditions for rescuing the dangerous situation.
water level lowering
Both sides are blocked at the same time
From the night of 12th to the early morning of 13th, the rescue team composed of PLA, officers and men of armed police, local government and all walks of life continued to rescue the breach, and the first thing to be solved was to open a road through which large vehicles and machinery could pass.
With the decline of the water level of the Mihe River, the accumulated water on a road outside the river bank gradually receded in the early morning of the 13th, and this road can lead to the breach position at a closer distance. The headquarters temporarily adjusted the plan, quickly opened the road, and the original road continued to be repaired, and a workbench for vehicles to turn around was built at the breach position. As a result, the speed of transporting emergency materials by vehicles is obviously accelerated.
"At about 6 o’clock in the morning, we found that the water level at the breach position dropped and the flow rate dropped to 10 cubic meters per hour, so we immediately decided to adjust the initial emergency plan on the assault boat to improve the efficiency of emergency repair." According to experts from the Yellow River Affairs Bureau of the province, the previous plan was to "wrap the head" at the breach to prevent the breach from continuing to collapse, and then pile at the breach, throwing rescue materials such as steel cages and stones, and finally closing the dragon.
With the formation of favorable factors such as water level drop, the scheme was changed to directly throw emergency materials at the breach position by large vehicles, and cooperate with bulldozer operation to directly block the closure. At 8 o’clock in the morning on the 13th, both sides of the breach were blocked at the same time. After a morning of emergency rescue, the breach of more than 80 meters gradually narrowed to about 40 meters.
Truck after truck.
The riverbank advances 5 meters an hour.
At about 3 pm on the 13th, the Mihe River at the breach position was basically at a standstill, which created very favorable conditions for plugging. However, because there is still intermittent light rain falling, vehicles carrying emergency materials often slip on the river embankment road. It’s only about two kilometers away, but it takes more than ten minutes. Some vehicles can’t even run, so they have to call a side excavator to help them get out of trouble.
At 4 o’clock in the afternoon, with the suspension of rainfall, the rescue efficiency was significantly improved. Large vehicles with a load ranging from 20 to 50 tons drive to the breach in an orderly way, dump the materials, and then pave them with bulldozers, and the speed is accelerating. According to the on-site personnel, one side can advance about five meters per hour.
Cao Chunguo, a bulldozer driver, has been on the riverbank since the afternoon of the 12th, with almost no rest in the middle. He grabbed the access road first and then took part in blocking the rescue. At the crevasse position, it advanced about 30 meters a day. Cao Chunguo introduced that when they advanced to the breach position, the water level had dropped, the water flow was not very urgent, and the materials thrown in could basically effectively build the river bank.
At the same time, officers and men of the People’s Liberation Army are constantly patrolling the river banks, cleaning and strengthening the dams in time, and checking whether there are hidden dangers such as piping.
After the levee is closed.
It needs to be raised and widened
At 5 o’clock in the afternoon on the 13th, there was only the last ten meters left in the execution port. Due to the deep water in the center of the breach, the progress of plugging slowed down. "There is a U-shape in the middle of the breach, and the water depth is more than 4 meters. If a car goes down, it will basically be invisible."
At 8 o’clock that night, the west bank of Mihe River in Yingli Town burst and successfully completed the closure. "Breaking the dike and closing the dragon does not mean the end of the rescue. Next, the river embankment of Helong will be raised and widened immediately, and an impervious layer will be made to make the river embankment play a role in resisting floods." Experts say that even after the completion of this series of work, the river bank here is still a temporary river bank. After the flood season, it will be demolished and a new river bank will be built according to the standards.
It is also known that there are three breakwaters in Mihe River, and another execution exit is still in emergency rescue on the east bank not far from the upstream. However, due to road reasons, the river embankment can only be constructed unilaterally, and the progress is relatively slow. However, according to the on-site personnel, the closure will be completed on the evening of the 13th.
Another breach in Yangkou Town is also under intense emergency rescue. Officers and men from the Weifang detachment of the Armed Police Force have been stationed for three consecutive days to block the breach and reinforce the levee. It is reported that the execution port is expected to complete the closure on the evening of the 13th.
Know the danger
Driving a truck for spontaneous rescue
On the 13th, on the provincial highway outside the dike of Mihe River in Yingli Town, Shouguang, the vehicles that came to participate in the rescue were still full. Many of the large trucks carrying emergency materials came spontaneously.
Chloe Wang, a villager from qian wang cun, Sunjiaji Street, Shouguang, learned of the breach of the Mihe River in Yingli section through WeChat group. He drove his truck to Shouguang to load materials and drove all the way to the emergency location. "As far as I know, there are more than a dozen cars coming from our side. Everyone came spontaneously after seeing the news." Chloe Wang said that before he came to Yingli Town, he first participated in the emergency rescue in his village and transported stones to repair roads.
Previously, Chloe Wang drove his own truck to transport building materials at several construction sites, earning 800 yuan a day to 1000 yuan. After the typhoon came, he took the initiative to participate in the rescue without compensation. "It is not easy for ordinary people. We, young and old, have come to help."
There are not a few social vehicles like Chloe Wang who actively participate in emergency rescue. It is reported that Changle’s Baotong Construction Investment Group mobilized more than 100 large trucks to participate in the Mihe rescue. (Qilu Evening News Qilu Yidian reporter Li Xiaodong Zhao Lei Zhang Yanyan trainee reporter Pan Zhengang Wang Yuwen)